

- #DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO MAC OS X#
- #DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO INSTALL#
- #DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO ZIP FILE#
- #DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO DRIVERS#
#DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO DRIVERS#
The '-alldrivers' option installs the file system drivers for rEFInd, which allows the boot manager to be able to access the Ubuntu kernel files on the Linux file system. The installation needs to be done in the Terminal, by running the install.sh script: There are other possibilities, but this seemed the easiest for me to manage - especially if something went wrong.
#DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO MAC OS X#
You'll want to check out the rEFInd installation instructions, but I chose the simplest option of installing rEFInd in the Mac OS X partition.
#DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO ZIP FILE#
See the rEFInd website for more information about boot managers and loaders, EFI and Grub.ĭownload the binary rEFInd zip file from and unzip it by double-clicking the file in the Mac OS X Finder. We'll then be loading Ubuntu using EFI instead of Grub, which means we can leave the old world of BIOS behind. So, for the Retina Macbook Pro I've switched to rEFInd, which is just a Boot Manager.
#DISK UTILITY FOR MAC NOT FOUND ON MACBOOK PRO INSTALL#
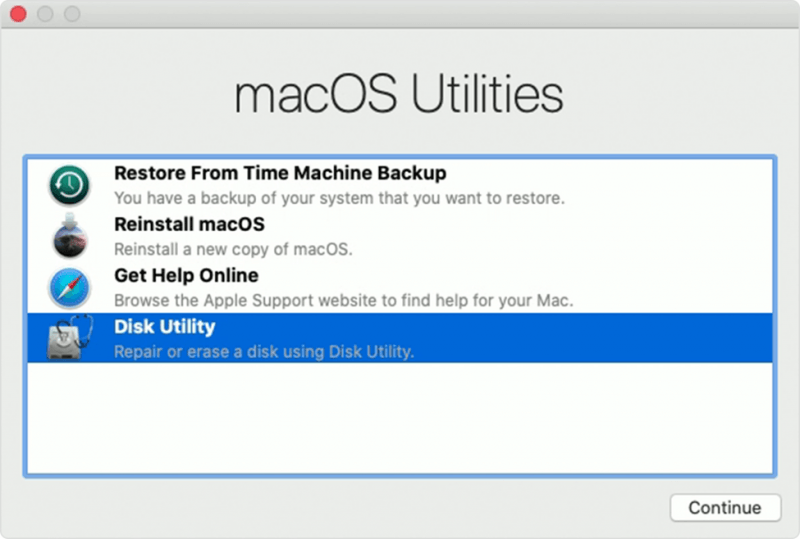
Install an EFI Boot Manager: rEFInd Previously, I've used Refit as a boot manager and boot loader for Ubuntu on a Mac, but that doesn't seem to be maintained any more. Note: unlike some disk image files, Mac OS X cannot mount the disk image, but it will boot fine from it.ģ. Instructions for creating a bootable USB stick are provided, you'll just need to remember to use the latest ISO that was downloaded above. Create the Ubuntu USB Installer The latest stable release of Ubuntu is available at - y ou'll need the 64-bit Mac (AMD64) desktop image. Disk Utility allows you to create a new partition with the extra space, but I just left it as Free Space, so that it would be created by the Ubuntu installer.Ģ. From there the Mac OS X partition can be resized. Just launch Disk Utility, click on the laptop's hard drive and click on the Partition tab. Partition the Hard Drive This step is nice and easy on the Mac. I've included some instructions on that in the post.ġ. This post outlines the full installation instructions, but if you already followed the previous guide, you can update the rEFInd installation and configuration file. Fortunately, there is a better way! Thanks to a comment on the rEFInd website, I found out that file system drivers can be installed that allow rEFInd to read the Linux partition. This then becomes a painful process that needs to be repeated every time there is a kernel update on Ubuntu. One of the challenges of the installation was that the boot manager, rEFInd, needed the Linux kernel to be copied from the Linux partition to the Mac OS X partition. In my previous installation guide, I outlined the first way that I found of installing Ubuntu on a Retina Macbook Pro. Please check the rEFInd website for more details. If you used Disk Utility from macOS Recovery, you can now restart your Mac: choose Apple menu > Restart.Update: If you have Mac OS X 10.10 (Yosemite) installed, then the rEFInd installation needs to be handled differently.

The order of repair in this example was Macintosh HD - Data, then Macintosh HD, then Container disk4 and then APPLE SSD. Keep moving up the list, running First Aid for each volume on the disk, then each container on the disk, then finally the disk itself.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
